Description of contact residues
A pocket descriptor, Ds, for a particular property s is computed as
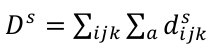
The descriptor dsijk in each grid vertices' ijk for the pocket function ρ(ijk) is computed as
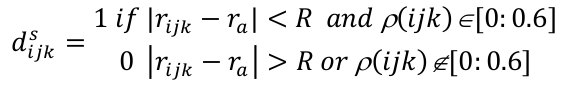
The 0.6 found in the equation corresponds to the default value of the iso-value used for pocket identification.
More information regarding this parameter can be found here.
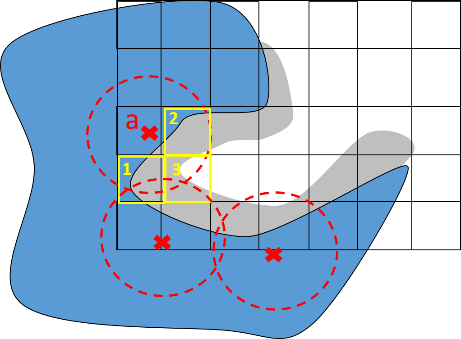
R = 3Å (angstroms) is the interaction distance and the region of ρ(ijk) ϵ[0:0.6], which describes the pocket layer where a protein-ligand bond can be formed if an atom of the ligand is placed in this position.
This table describes the residue and atom type that is associated with each descriptor.
| Descriptors | Residue Type | Atoms Type |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Residues (Pos.Res.) | HIS | ND1 |
| LYS | NZ | |
| ARG | NH1 | |
| ARG | NH2 | |
| Negative Residues (Neg.Res.) | GLU | OE2 |
| ASP | OD2 | |
| Hydrophobic Residues (Hydrophobic Res.) | VAL, ILE, LEU, MET, PHE, TRP, CYS | All heavy backbone atoms |
| Aromatic Residues (Aromatic Res.) | PHE, TRP, TYR, HIS | All heavy backbone atoms |
| Polar Residues (Polar Res.) | GLN, ASN, HIS, SER, THR, TYR, CYS, MET, TRP | All heavy backbone atoms |
| H-bond Donors | ARG | NE, NH1, NH2 |
| GLN | NE2 | |
| HIS | ND1, NE2 | |
| LYS | NZ | |
| SER | OG | |
| THR | OG1 | |
| TRP | NE1 | |
| TYR | OH | |
| H-bond Acceptors | ASN | OD1 |
| ASP | OD1, OD2 | |
| GLN | OE1 | |
| GLU | OE1, OE2 | |
| HIS | ND1, NE2 | |
| SER | OG | |
| THR | OG1 | |
| TYR | OH |